Analyse consumer behaviour
About the Unit
Business success is all about the consumer. This module will help you determine what drives consumers to purchase your product or service over your competitor’s. It will help you establish the most effective marketing channels for your target market, so you get more “bang for your buck.”
You will learn about digital marketing in the modern world and the importance of having structure, procedures and marketing objectives to keep you focused on the end goal which is SUCCESS.
Start with the Study guide BSBMKG435.
Do you know what your consumer needs?
Learning Outcomes
BSBMKG435- Analyse Consumer Behaviour
- Identify and evaluate the drivers of Consumer behaviour.
- Evaluate the reasons behind existing levels of consumer interest.
- Recommend a marketing focus to reach the target market of the business venture.

Click on tabs for Learning Content
It is All About the Consumer!
Understanding what makes them buy and the psychology behind the decision- making process will help you sell more.
Marketing is about solving your customers problems, offering them the solutions and selling the benefits not the features of your product or service.
The customer wants to know:
What’s in it for Me?!?”(WIFM)
Can you describe your business in one sentence?
An “elevator pitch” describing:
- what you do
- what outcome you achieve
- what problem you solve
will help you network and gain focus on your business.
Understand your Product and your Consumer.
➡ Review Knowledge Question 1a,b,c & d.
For a successful business, product knowledge is key. Understanding your products’ features and benefits allows you to tailor your language to meet the customer’s requirements.
You need to know:
- What problem you are solving.
- The benefits your product or service offers your clients.
Understanding the motivation behind why your consumers want to purchase, what segment out of the whole population is interested and how to solve their problems better than your competitors will all lead to business growth and success.
What industry are you in?
An industry is a group of organisations involved in handling the same type of product or service.
Examples of industries include:
- Publishing industry
- Tourism industry
- Retail industry
- Manufacturing Industry
➡Review Knowledge Question 1a
What are the Features and Benefits of your product/service?
Features are the physical facts about the product/service. Benefits are what is the advantage to the customer.
- The Feature is the products purpose, the Benefit is that it will deliver a productivity increase to your business.
- The Feature is how it works. The Benefit is it is easy to use.
- The Feature is how it is delivered. The Benefit is you don’t need to pick it up.
➡Review Knowledge Question 1b
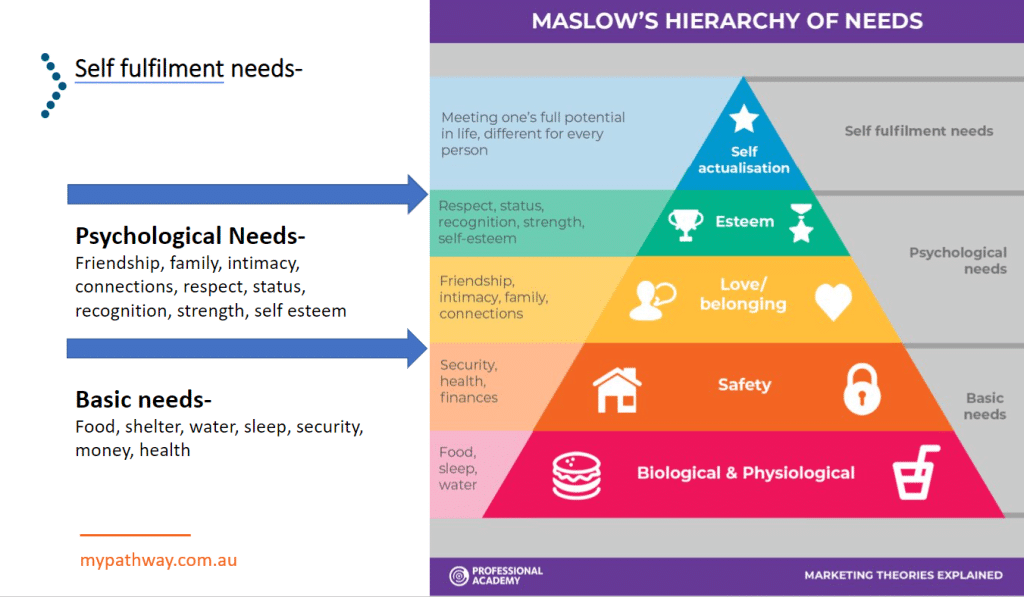
Why is there a need or want for your product/service?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (below) displays a pyramid indicating humans different needs and the level of importance they place on these.
His diagram shows that people tend to look after their basic needs of food, shelter, water, money, health and security before they can consider their psychological needs of love and belonging.
His theory may not apply to everyone. Most people agree that you need food, shelter and security before you spend money on wants.
However, if you were an artist, you might choose your creativity or self fulfilment needs over finances and security.
Needs are the essential things for us to survive such as water. Wants are what we would like such as a soft drink.
Needs can be physical, social or individual. The advancement of technology has altered many wants to needs. An example of this is mobile phones. I would suggest that mobile phones are now a necessity in life, where years ago they were a want.
Demand is the ability to buy the wants and needs. If you want something and you can afford to buy it, then there is the demand.
➡Review Knowledge Question 1c
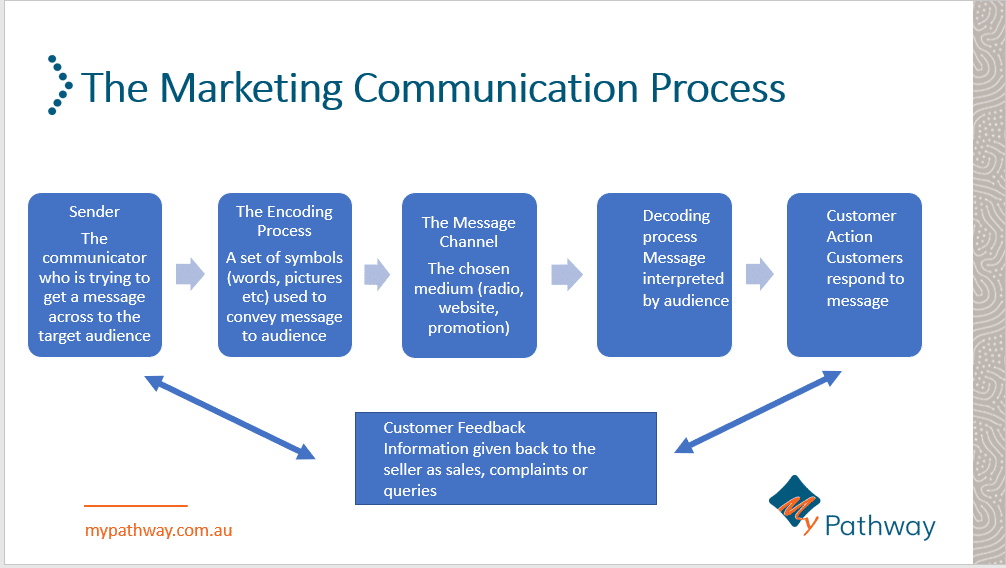
Marketing Channels
- are tools or platforms that we use to communicate to our audience
- we use these to reach our audience where they hang out (social media, google search) or reach them directly (text messages and emails).
- the channel you choose depends on where your customers are looking
Non-digital marketing channels include:
- direct selling- face to face
- network marketing- join industry associations
- catalogues posted direct to client
- events- market stalls, trade fairs
- flyers
- business cards
- car advertising
- branded uniforms
Any channel that does not use technology is regarded as non-digital marketing. These can be just as effective as digital marketing.
***Remember- it depends where your customers are looking.***
Digital marketing channels include:
- organic search engines
- social media
- video marketing
- paid advertising banners
- email marketing
- conversational marketing- live chatbots, messaging apps and social media
- Word of Mouth marketing- online reviews
- Podcasts- conversational marketing
➡Review Knowledge Question 1d
➡Review Knowledge Question 2a
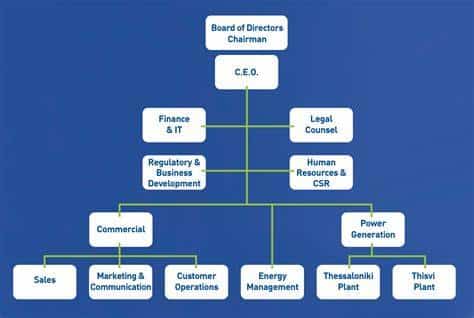
Organisational Structure
An organisational structure defines each employee’s role and how they fit into the whole organisation.
An organisational chart is a diagram that outlines the chain of command and communication channels. It helps clarify who is responsible for the different areas of the business and directs you to the person you must speak to if you need advice or assistance.
As your business grows and you take on staff, you will need to delegate responsibilities to others and implement processes or procedures.
Marketing is often a specialised field that you may choose to outsource. This is your communication channel to your customer and your brand and reputation rely on your marketing to increase sales.
Clear processes outlining your style or brand, what message you want to convey, what method/s you use, how often you promote your business will all need to be put into your marketing strategy and communicated and implemented to the correct people.
You can’t have everyone posting whatever they like onto your social media page. There needs to be a clear strategy and process in place. Your social media page is your shop window. It is your customer’s first impression of your business. It needs to be maintained and be commercial at all times.
An example of a hierarchical organisational chart
Procedures are the process.
➡Review Knowledge Question 2b
A procedure is a list of detailed steps on how to implement a policy. Procedures ensure all employees consistently meet the objectives and goals of the business.
Your Social Media Manager would have a social media Policy to protect the company’s brand and image. The policy would be based around the law and the procedures are the process to be followed to ensure no rules are broken.
The procedure (HOW) would include information on the approval process of all postings onto the social media page. The procedure is to be communicated to all staff so they remain compliant with the rules and regulations of the business. This procedure will protect the integrity of the business.
➡Review Knowledge Question 2c
Marketing Objective
The marketing objective is the steps you take to reach your big picture Marketing goal.
An objective needs to be SMART.
S-Specific
M-Measurable
A- Achievable
R- Realistic
T- Time bound
These objectives are used to measure your results after the marketing campaign has finished. It could be measured by increased sales/ increased conversion rates/ increased brand awareness.
Choose your objectives, set how you will measure your results, give it a timeline so you can review your results in the future.
➡Review Knowledge Question 2d
Key components of marketing communication
The 4 marketing communication concepts are:
- Know your target audience and who you are communicating with.
- Know your message- what is your objective?
- Select your communication channel/s
- What is your unique selling point or point of difference?
This is explained further below:
- Know your target audience. In all communication there is a sender and a receiver. In marketing the seller is the sender and the customer is the receiver. This is why it is imperative that the seller understands who their customer is so they can get their message out there effectively.
- Communicate the business through advertising and promotions. The sender uses images, words, symbols to convey a message to the audience using a chosen method. The method chosen will depend on where the audience is looking. The message conveyed needs to meet the marketing objective and accentuate the point of difference.
- Feedback is given in the form of purchasing, enquiries or recommendations. The customer decodes and interprets this message and decides how they are going to respond. Whether they buy or not.
Want to learn about digital marketing? There are loads of free courses on “Google Digital Garage Australia”.
Watch this video to learn more:
Digital Marketing Methods
Mateusz Makosiewicz states that “Businesses use different means (content, messages, ads) to reach their audience in places where they hang out (e.g., social media, Google Search) or reach them directly (e.g., text messages, emails). They may use a selection of channels or all available channels. ”
There are digital and non-digital channels to choose from. digital channels are those methods used that require technology to communicate the message. Examples include:
- Organic search- Search Engine Optimisation(SEO) -the google search.
- Social media- Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, Tiktok, LinkedIn
- Video marketing- YouTube, Tiktok, Reels
- Digital advertising- paid banner ads
- Email marketing- digital direct marketing
- Sponsorship on a website your customers use
- Conversational Marketing offered on websites for real-time conversations. (Chatbots)
- Word of Mouth(WoMM) online reviews
- Podcasts- content marketing
- Events- are becoming more virtual
- Affiliate marketing
➡Review Knowledge Question 4
Get your business found on Google- watch this video
➡Knowledge Question 3&4
Analysing customer’s digital behaviour.
Every time, we go online we leave our digital footprint. Many online sites leave cookies on our system, which allows our movements from site to site to be tracked. Every part of our online history can possibly be tracked by databases or viewed by other people.
This information is useful to business. The end goal of every digital footprint marketing campaign is to increase business revenue through the business website.
Analytics helps you understand how people use your sites so you can improve them and increase your conversion or sales.
You can use the analysis to predict future results and see how customers behave online by tracking their customer journey.
Google analytics is one option you could use.
➡Review Assessment 2/Task 4
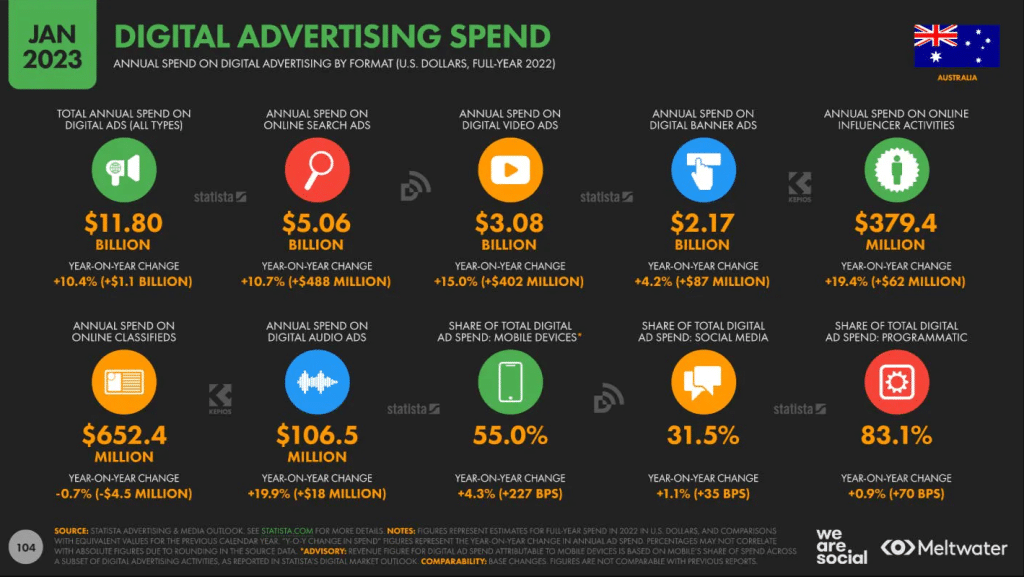
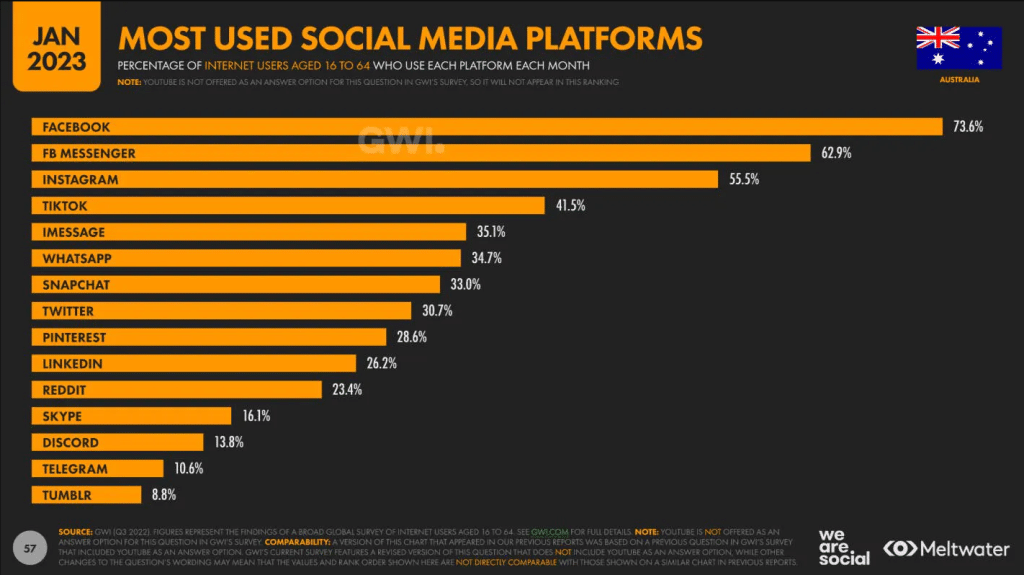
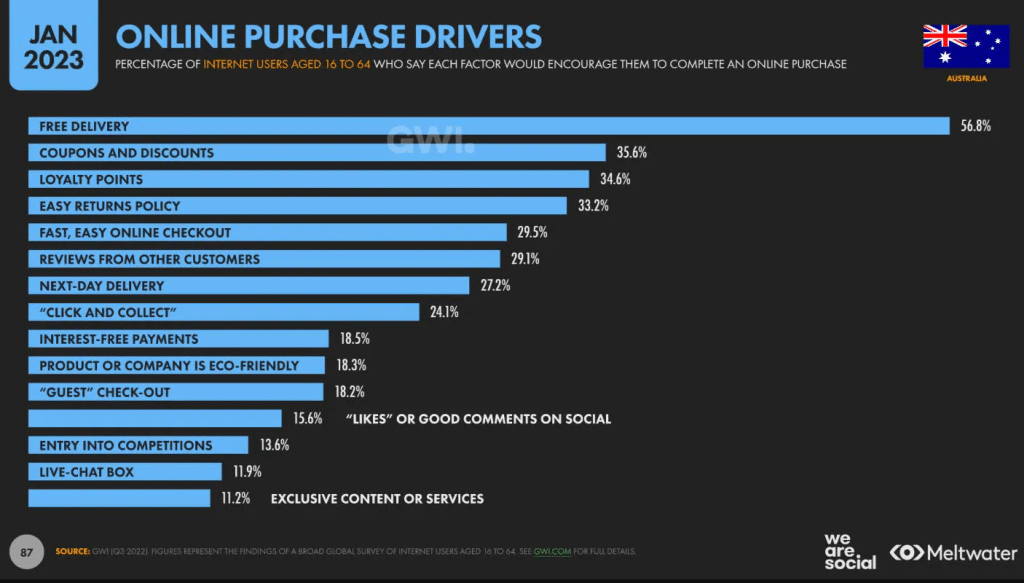
Review customer digital-interaction data
You need to reach your customers where they are looking. Your retirees are unlikely to be using TikTok or LinkedIn.
There are several sites available below that can provide data on the most popular sites for which demographic.
- What are the key words that people are searching for?
- What questions are they asking?
- What items are they searching for?
All of this information will help you determine your future business demands and possible marketing opportunities.
Take a look through these:
Assessment 2- Task 1
Business Feasibility Study
You may have completed this in a previous unit.
What really influences customers to buy?
Watch this video to understand the psychology of purchasing.
Connect to your Consumer
➡Assessment 2 Task 2
Consumer Types/Target market
a) Agreeable consumers
b) Commercial Consumers
c) Conscientious Consumers
d) Discount Consumers
e) Discretionary Spending Consumers
f) Extroverted Consumers
g) Impulsive consumers
h) Inferior goods consumers
i) Loyal consumers
j) Luxury Goods Consumers
k) Need- based Consumers
l) Neurotic consumers
m) Open Consumers
n) Personal Consumers
o) Seasonal Consumers
Click on the 3 boxes below for 3 examples of consumer types.
Discount Consumers
- These customers only buy when something is on sale or offered at a discount.
- Social media, direct mail is an effective advertising strategy for this group.
- Make sure you commuicate the savings
Impulsive consumers
- They purchase on a whim, don’t often shop for a particular service or product in mind.
- Impulse buys are usually not logical decisions but emotional ones.
- marketing messages need to consider emotions and the reasons for buying
Discretionary Consumers
- Have a lot of discretionary income to spend.
- Teenagers will still spend because they don’t have any bills.
- A stable and reliable consumer group, you should reach on a regular basis
Appeals in advertising
Appeal is “Your communication needs to appeal to people because you are credible, you affected their emotions or you made logical sense”(VCG Blog, The Visual Communication Guy, Newbold Communication & Design)
Examples include: Sex appeal, Brand Appeal, Bandwagon Appeal, Endorsement appeal, Humour Appeal, Fear appeal, Less than perfect appeal, Masculine/Feminine appeal, Music appeal (jingles), Personal (Emotional) appeal.
Watch these 3 videos and identify what appeals they use to connect to the consumer.
Processes to consider when promoting your product or service.
When communicating your products and services to your consumer you need to be aware of cultural and ethical considerations and best practice.
For example: Is the Old Spice advertisement suitable for all cultures and age groups? Could it be considered sexist or offensive to some people? Is it misleading or false advertising? Does it comply with Australian Consumer laws and Anti-discrimination laws?
Email marketing campaigns need to consider the Privacy act and SPAM act. What processes do you have in place to make sure these laws are not breached?
Digital marketing rules and regulations change regularly so you need a process to stay informed.
Any promotional activity needs to be monitored and controlled. This is your brand and reputation at stake. You can’t have anyone and everyone posting whatever they like to your social media page. A clear process and chain of command needs to be in place, with an authorisation process in place to ensure you maintain a strong brand awareness to your audience.
Assess the capability for the business to keep up with any changes in demand.
Capability is whether you can do something. If your business demand increases, are you capable of keeping up with demand?
Capacity means meeting the needs of the customers without wasting resources. “Capacity” is the number of customers you can serve in an hour or the number of products you can make in a month. Sometimes you may need to adjust your capacity to meet changing customer demand or be flexible with your capacity due to the unpredictable nature of business.
To optimise capacity you need to understand customer demand and predict when and why it might change. Restaurants get busy at meal times and toy manufacturers get busy at Christmas.
- Look at your sales forecasts. If sales increase buy 10%, 20%, 50% what actions do you need to take to make sure your business can meet demand.
- Take stock of the resources you have available. If demand was to increase, how quickly can you obtain more stock? Do you need to source some alternate products or suppliers to help meet the gap?
- Staffing and labour hire- do you need help to meet the increased production? Do you have an outsourcing company you can turn to in an emergency?
- Cash- do you need to consider a loan or an investor to provide extra cash to buy the extra resources required.
- Machinery, Plant and equipment- are your current PP&E well maintained? Can they handle the increase in demand. Do you need to organise an upgrade in your equipment. Could you hire extra equipment? Can technology help take some of the strain?
- Location and storage-Do you have the space to store extra materials? Do you have the facilities for extra staff?Is your location easy for you to distribute your goods and services?
Assess your business now. Have your contingencies ready. Don’t get caught out and be floundering if you get a sudden increase in sales. Monitor your figures regularly, stay informed of industry changes and trends so you can be prepared.
Evaluate reasons for existing levels of consumer interest: Measure your current demand
Analyse your results against your forecasts:
- number of items sold each week
- busiest times and days of visitation
- visitation versus conversion
- number of work requests received per month
Understanding what is selling well and identifying possible trends will help you plan your resources and be prepared for increasing sales. Looking across 12 months will highlight long term trends, whilst shorter time periods will help you analyse seasonal events like Christmas.
Analyse your Marketing plan:
- Analyse your results from your promotions
- Analyse your customer feedback and customer reviews
- Do you have any marketing campaigns that might increase the sales?
- Conduct a customer survey about a product or service to gain more insight into why they buy.
- Speak to suppliers and gain insights on trends in the industry
Analyse consumer responses through analytics and the customer journey.
Google Analytics can offer insights into your customer’s digital shopping journey.
- How do they use your website?
- What key words and questions are customers asking.
- It can offer real time reports that analyse the peak times consumers visit your site etc.
Use this site to gain valuable knowledge about your customer’s journey to help you improve your sales. Having this knowledge can help you plan.
Analyse these points to determine what opportunities there are for you to increase the demand of your product or service.
If it works and you get really busy, is your business prepared? You do not want to disappoint your loyal customers who have advocated your product to their friends by running out of stock or letting your quality drop.
Customer Journey mapping will help you analyse your touchpoints and ensure your customers are happy every step of the way.
Plan to monitor any changes in business demands.
- Is your business growing?
- Is your customer base expanding?
- Are new competitors entering your market?
Think about any factors that may affect demand now and in the future. Consider your PESTLE Analysis and the factors that may affect your business, like technological advancements or legislation changes.
- Develop a procedure that allows you to check in regularly with sales results.
- Conduct regular competitor analysis.
- Stay informed on current affairs and economical changes.
- Diagram common scenarios that affect demand.
- Designate a time to regularly plan and forecast the future demands of your business.
- Identify why there is rapid growth. Have you had a marketing campaign that has been successful? Review all marketing campaigns to identify your customers.
- Review customer feedback regularly.
Review your processes, can technology help?
Proposed Actions and Processes to Respond to Changes in Business Demand.
Document 4- Assessment 3- Business Plan Instructions
- Write your full name on the top of the first page “Participant name:”
- Attach a completed copy of your Operational Plan to be marked.
- Attach the completed parts of your Financial Plan that are requested.
Check off the Assessment Submission Checklist
This will ensure you have completed all tasks and paperwork correctly and we won’t need to return anything before marking
News feed