Establish legal and risk management
requirements of new business ventures
About the Unit
Know what your legal obligations are, what business structure best suits you and how to negotiate and write binding contracts. Determine any possible risks to the business, find specialist help and reduce any possible breaches resulting in litigation, fines or loss of reputation.
Start with the Study guide BSBESB402
What is the difference between an Act, a Regulation, a Code of Practice and Standards?
Learning Outcomes
BSBESB402- Establish Legal and risk management requirements for new business ventures
- Identify legal and risk management requirements relating to your business
- Develop and Implement procedures and processes to comply with legislative and regulatory requirements.
- Negotiate and arrange contracts
- Mitigate Business risks

Click on tabs for Learning Content
Legal Considerations for New Business
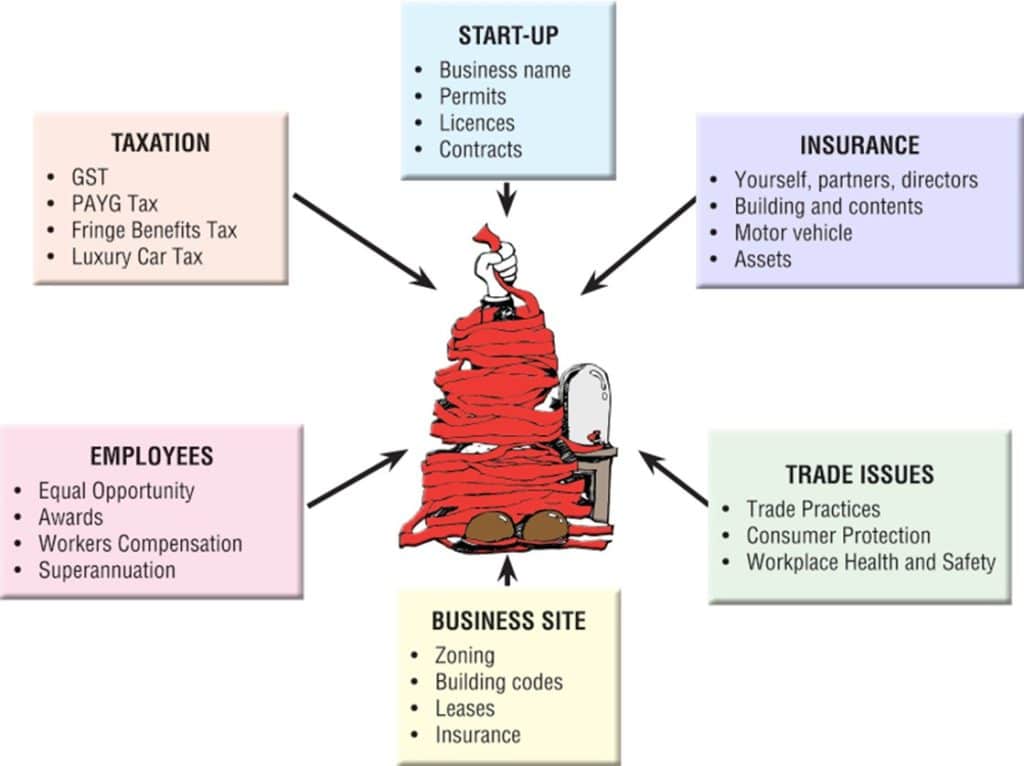
Other areas to consider:
- Marketing legislation
- Business Ethics
- Intellectual Property
Legal Essentials in Business
There are many risks in business and one way of avoiding litigation or hurting someone is to be aware of all the different laws, regulations and standards you are required to follow. Depending on your business will depend on what laws apply to you.
The link below offers advice from the Australian Government on the common laws new business need to comply with such as registrations, contracts, marketing and employment.
Legal Obligations for Online Businesses
Intellectual Property Basics for Business
Australian Consumer Law (ACL)
The following videos explain Australian Consumer Law and Consumer guarantees.
- What are the consumers rights?
- How must you comply with ACL?
- What do you as a supplier have to guarantee your customers?
- If you fail to provide this, what rights do the customers have?
➡Review Knowledge Question 1
Industry Codes of Practice and Standards
Industry codes of practice and standards are written by industry for industry. They are based on legislation and law but are not written or implemented by the government. They can be mandatory or voluntary, depending on the industry. They are usually quicker to implement than legislation.
Examples of Industry Codes of Practice
Four examples of mandatory industry codes of practice are:
- Franchising Code of Conduct
- Horticulture Code of Conduct
- Oil Code
- Retail Grocery Industry Unit Pricing Code
Further information and guidance on the current prescribed industry codes can be found at the ACCC’s website, www.accc.gov.au.
➡Refer to Knowledge Question 2
Environmental Law
There are many advantages to managing the environmental impact of your business. Having an Environmental Management System (EMS) can benefit your business by:
- improving your reputation
- lowering your risk of fines
- lowering your costs
- creating a competitive marketing advantage
- providing focused, knowledgeable and motivated staff
- reducing waste and improving work processes
Every state has their environmental laws to comply with. states Check your local websites for information.
➡Refer to Knowledge Question 3
Your Responsibilities under the WHS Act- watch this video.
Workplace Health & Safety Act
As a sole trader, you do not have staff and are therefore not required to follow the WHS Act. This is why you are required to have Public Liability insurance. This is to protect you if someone injures themselves or you cause injury to others.
However, it is important you understand your responsibilities in case you do need to hire staff. It is also good to follow safe work practices to protect yourself from injury. Your business needs you fit and healthy.
Every state has their own website full of free information and advice.
➡Refer to Knowledge Question 4
Industrial Relations or Employment Laws
As a sole trader, you may not have staff, however, it is important to understand the legal requirements if you were to hire staff or contractors in the future.
➡ Refer to Knowledge Question 6
Insurance & Coverage
Insurance can reduce your risk factors by allowing you to recover quickly from unforeseen circumstances.
Types of Business insurance can include:
- Public Liability
- Professional Indemnity
- Income protection insurance
- Total & Permanent Disability
- Business interruption
- Stock, products and asset insurance
- Technology and cybercrime
- Workcover (if you have employees)
It is important to have the correct coverage. You do not want to be underinsured and left paying expensive bills.
If you are a sole trader, you may require public liability insurance, professional indemnity or income insurance. Most businesses will not let a contractor on site unless they can prove they have a minimum of $10 million coverage of public liability insurance.
➡ Refer to Knowledge Question 5
Taxation Legislation
Failure to comply with taxation law could result in fines, penalties and possibly imprisonment.
You need to develop an effective record keeping system which is well organised, easy to access and secure. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) have clear rules and regulations on:
- what records you are required to keep
- how to keep them
- how long to keep them for
- how to delete them
You can choose a digital or manual record keeping system.
Watch the video and read the “5 Rules of record keeping” article on the ATO website to learn what these requirements are.
➡ Refer to Knowledge Question 7
Registration & Licensing.
The Australian Business Licence and Information Service (ABLIS) helps you find the legal compliance requirements for your business.
Use the link below to identify what your obligations are under Australian Law.
➡ Review Knowledge Question 14.
Privacy & Spam Laws for Small Business
Business structures
Before you can understand what your legal responsibilities are, you need to establish your business structure. There are Pros/Cons to each, and these 4 videos explain what these are.
In Australia, the four most popular forms of business structure are Sole Trader, Partnership, Company or Trust. Click on the link below to find which one suits you best.
➡ Click on the videos then work through Question 12
Contracts are required in business. Examples include:
- Lease agreement
- Sub contractor agreement
- Supplier agreement (Bill of sale)
- Service agreement (Bill of Sale)
What makes a contract legally binding?
For a valid contract whether verbal or documented, the following elements must exist:
- a legality of purpose
- an intent to create legal relations,
- an offer,
- an acceptance,
- a consideration,
- the consent,
- a documented form
Click on the button below to read more:
➡️Refer to question 8b
1. How to negotiate a contract.
When negotiating contract terms from your suppliers you may need to write a supply agreement. When doing this, you need to consider “the 5 Rights to Procurement.”
Ask yourself, can your provider offer you:
- The RIGHT price?
- Deliver to the RIGHT Place?
- at the RIGHT time?
- at the RIGHT quality?
- and the RIGHT quantity?
Also consider the RIGHT source.
2. How to write a contract.
➡ Complete Assessment 2- Project 1- Task 1 & Task 2
3. How to end a contract
➡ Refer to Knowledge Question 8
Contracts are required in the Purchasing & Procurement process.
Procurement is the acquisition process that starts with:
- determining the resources you need to acquire
- investigating possible suppliers who can provide you these.
- obtaining quotes and proposals for price and specifications. (the 5R’s)
- negotiating and defining service level agreements
- selecting a vendor
- creating a purchase order
- managing shipping
- receiving invoices
- making payment
➡Refer to Knowledge Question 9
Contracts will also need to be negotiated when leasing or buying Property, Plant or Equipment.
➡Refer to Knowledge Question 10
When should I manage risk?
Risk Management is an ongoing process. You should schedule review dates, or whenever there are changes in your business such as when you:
- start or buy a new business
- change procedures on how you do something
- purchase new equipment or substances
- WHS regulations change
- concerns are raised by others
- new information comes to light
- responding to a near miss or incident report
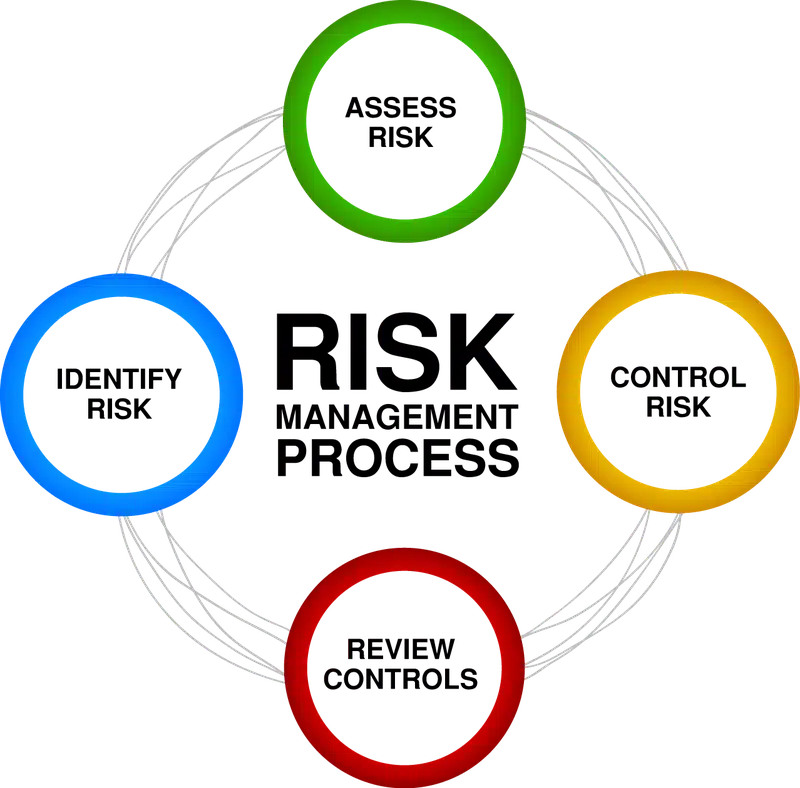
The Risk Management Process is 4 STEPS:
- IDENTIFY the Hazards (anything that could cause harm)
- ASSESS the risks by likelihood vs consequence (using the Risk Matrix)
- CONTROL or Eliminate the Risk (the Hierarchy of Needs)
- REVIEW your Control measures (Action Plans)
(Refer to BSBESB401- Research & Develop Business Plans where we covered this previously)
➡Knowledge Question 15
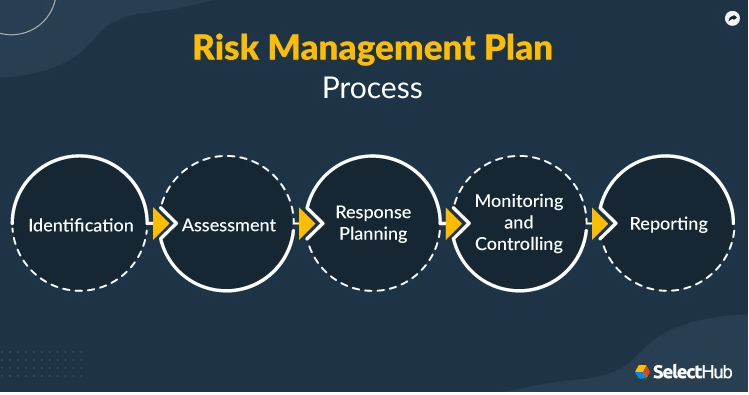
The 5 parts of a Risk Management Plan
➡Review Knowledge Question 15
There are 5 elements to a Risk Management Plan.
- Identification
- Assessment
- Response Planning
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Reporting
Refer to the article in the link below which explains this process thoroughly
1 & 2. Identifying and Assessing the Risk.
This video explains how to use the Risk Matrix to determine the level of risk and the priority needed to control it.
3. Response Planning
The main objective of any investigation is prevention.
Investigation procedures need to be put in place to ensure the cause of the incident is found based on facts. The use of a systematic process such as a checklist or incident report form can help this process remain unbiased. Once the cause has been established, then a plan can be developed to prevent the risk from happening again.
Click on the link below to learn more:
➡Review Knowledge Question 12
4. Monitoring and controlling your Risk
Investigating non-compliance and taking corrective action
When it becomes apparent that non-compliance has occurred, you need to investigate how and why this has happened. It will highlight that your current risk management plan has not mitigated your risk effectively and you may need to implement some corrective actions to prevent it from happening again.
You may fail to pay a tax bill on time and the Taxation Department contact you threatening you with a fine due to non-compliance.
Step 1: Investigate
a) are their claims true and accurate based on your research?
b) how did you fail to pay this bill on time?
c) what are your current processes that you follow?
d) what is the identified gap that has allowed this payment to be missed?
Step 2: Corrective Actions
a) Now you have identified why this happened, what steps will you implement to prevent this from happening again?
Controlling your Risks
Strategies, Processes and Monitoring
➡️Refer to tab “Project 3” for more information
Procedures & Processes
In order to mitigate risk you need to put some policies and procedures in place. Failure to comply can result in:
- fines
- imprisonment
- death or harm to others
- business closure
- litigation
- loss of business reputation
- increased insurance premiums
Procedures are the HOW you will make it happen. You now know the laws and regulations you are required to follow. Now it is your responsibility to ensure you have the processes in place to protect your business and yourself. You need to write policies and procedures to clearly communicate to others how to remain compliant and prove your due diligence if something was to go wrong.
Child Care is a high risk industry. This video is a great example of Best Practice for implementing and maintaining policies and procedures.
How to write a procedure
Watch this video on how to write a procedure, because you will be asked to write a procedure for your own business.
One example of procedures that every business needs is Record Keeping Procedures. Having an effective record keeping system for your financial records will ensure you:
- can monitor your business health
- meet your tax and superannuation obligations
- manage your cashflow
- plan for success
- apply for a loan if you need one.
Click on the link below to help you with Assessment 2
Strategies, Processes and Monitoring
A Strategy is your plan on how you will reach the required objective. In the case of Project 3- How will you meet your responsibilities and legal obligations for the mentioned legislation?
Processes are the way the task is to be carried out. It focuses on the steps you will follow or the actions you will take to meet your strategy. (procedures)
Monitor is the process of reviewing the actions taken. Have they been effective and achieved what you wanted to achieve?
example: Australian Consumer Law.
Business obligation: cannot make any false misrepresentations about product.
My strategy is to have a Communications Policy in place to control messages about my product.
My process is –
- design and implement a communications policy and procedures for all forms of communication, digital, verbal and written.
- train all new staff on these procedures
- develop and communicate an organisational structure outlining the chain of command.
To monitor this strategy –
- I will obtain regular feedback from customers, suppliers and other stakeholders.
- Regularly review any changes based on KPI’s.
➡ Review Project 3
refer to tab “Identify Legal Requirements” for WHS, ATO and Privacy
Document 4- Assessment 3- Business Plan Instructions
- Write your full name on the top of the first page “Participant name:”
- Attach a completed copy of your Small Business Plan as requested.
Check off the Assessment Submission Checklist
This will ensure you have completed all tasks and paperwork correctly and we won’t need to return anything before marking.
News feed



