Address compliance requirements
for new business ventures
About the unit
Compliance is ensuring your business follows all of its legal responsibilities. This unit will help you find which legislation is relevant to your business and how to meet compliance requirements protecting your business from litigation, fines, harming others or imprisonment.
Start with the Study guide BSBESB305.
What’s the difference between an Act, regulations and standards?
Learning Outcomes
BSBESB305 – Address compliance requirements for new business ventures
- Research compliance requirements for new business venture
- Seek specialist advice on compliance and risk mitigation
- Take action to support compliance in business

Click on Tabs for Learning Content
What is Compliance?
- Compliance is obeying rules and regulations set by industry regulations and government legislation.
- It is a business’s ability to adhere to standards, regulations, rules, policies, orders or requests.
- Compliance standards are legally binding and enforced by government agencies, and restrict the way organisations can conduct business.
As a business, you can implement a range of tools and processes to achieve compliance.
Legislation, Acts, Regulations, Codes of Practice and Standards
Compliance is all about following the rules. There is Legislation and Acts, Industry standards and regulations. What is the difference between all of these?
The video below explains it:
Research Compliance Requirements
There are many government and industry websites that supply current advice on legislation, regulations and industry standards. It is your responsibility as a business owner to stay well informed. Join newsletters and industry organisations to make sure you are aware of any changes that could affect your business.
Click on the links below to research legislation, rules and regulations for business to adhere to.
➡Review Knowledge Question 1, 2,3,7 & 9.
➡Review Question 8
Seek specialist advice on compliance.
Understand where you can get help. There are many specialists who offer services and advice to ensure you remain compliant in business. Some government agencies offer free advice. The Australian Taxation Office, Fairwork Australia and Worksafe Australia are three examples of organisations that offer educational support and templates you can use to keep your business compliant.
There are other professionals who can give helpful advice at all stages of the business cycle.
Who can help with my tax?
Answer
- The ATO
- Registered Tax Agent
- Accountant
- Some bookkeepers (if registered)
Who can help with finances?
Answer
- Bank Manager
- Financial adviser
- Accountant
- Bookkeeper
- Financial Counselling Service
Who can help with compliance?
Answer:
- Lawyer
- Government agencies-ATO, Worksafe, Fairwork etc.
- Industry/Trade Associations
➡Review Question 5 & 6
Insurance advice
It’s important to shop around for insurance and discuss what’s best for your business.
Business policies, processes, procedures and codes of practice.
Business Policies, processes, procedures and codes of practice can help you to:
- Minimise risk
- train your employees better
- comply with legislative and regulatory obligations
- improve your business operational efficiencies
- manage staff and customer expectations better
- work effectively with suppliers
Policies often link to the regulations. They are the why.
Procedures are the how you will implement the policy into your workplace. The procedure is a set of instructions on how you and your team will perform tasks so that they will meet the legislation and ensure you remain compliant.
This is a process that your team are expected to follow. Failure to follow policies and procedures could result in your business being adversely affected. You could be fined, lose your reputation, hurt someone or even be imprisoned.
This is why it is imperative to have processes in place to check that all policies and procedures are being followed. You might conduct regular audits or training sessions or do random spot checks. A well organised and documented process is beneficial as proof if you are ever audited.
➡Review Question 4 & 5
- consider 5 laws/regulations you are required to follow.
- write 5 procedures you will follow to make sure you stay compliant with these laws.
Example of how Policies, Procedures and processes work together:
ATO legislation states that “you must keep your receipts for 5 years.” plus other record keeping standards.
The Policy (Why):
Record keeping policy for taxation records as stated by the Australian Taxation Office.
The Procedure (How) for processing bank statements:
1.All business purchases need to be highlighted on the bank statement at the end of the month.
2.All bank statements must be filed at the end of every month in the “bank statements” folder in the One Drive.
3. saved as “document name- month- year”.
Your process
is to audit your records every 6 months to make sure that all procedures are being followed and you remain compliant.
Minimising Risk
In risk management we learn there is a cycle.
- Identify the risk
- Assess the risk
- Control the risk
- Monitor the risk
The same risk management process is to be followed when it comes to compliance.
- You have done your research and identified all the rules and regulations your business is required to adhere to. (Identify the risk)
- You have assessed the likelihood versus the consequences of what would happen to your business if you do not comply with the legislation. (Assess the risk)
- You have written a “Policies and Procedures manual” to reduce these risks. (Control the risks)
- Finally, you have processes in place to monitor if these policies and procedures are working. Are people using them and following them? If not, why not? What are the consequences or actions to be taken if there is a breach and your company is put at risk?
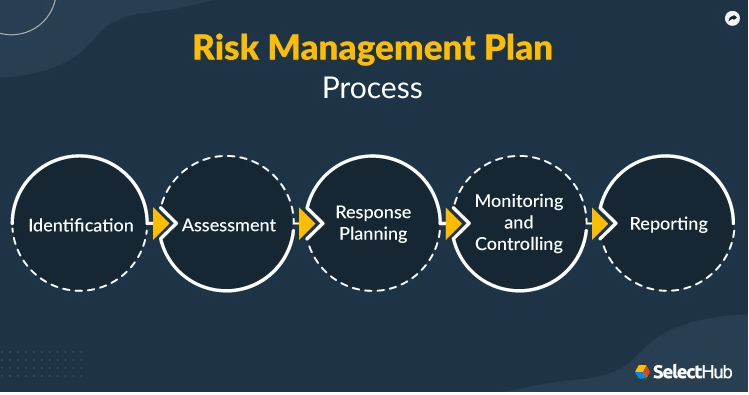
This process is an ongoing cycle that needs to be followed up regularly. Laws change, new staff start, old staff get complacent or the procedures are not practical and that is why people are not following them.
Your team culture also plays an integral part in compliance management.
- Encourage participation and open communication.
- Offer regular training sessions
- Gain regular feedback from those the procedures affect
- Promote a “Safety First” mentality
- Reward good behaviour
Investigating non-compliance and taking corrective action
When it becomes apparent that non-compliance has occurred, you need to investigate how and why this has happened. It will highlight that your current risk management plan has not mitigated your risk effectively and you may need to implement some corrective actions to prevent it from happening again.
You may fail to pay a tax bill on time and the Taxation Department contact you threatening you with a fine due to non-compliance.
Step 1: Investigate
a) are their claims true and accurate based on your research?
b) how did you fail to pay this bill on time?
c) what are your current processes that you follow?
d) what is the identified gap that has allowed this payment to be missed?
Step 2: Corrective Actions
a) Now you have identified why this happened, what steps will you implement to prevent this from happening again?
Control measures are the things you put in place to reduce risk and prevent harm. Control measures may include one or a mixture of:
- Removal
- Rules
- Procedures
- Equipment
- Exclusions
- Training
- Supervision
- Limitations
- Preventions
- Safe Work Methods
There are lots of control measures available.
Document 4- Assessment 3- Business Plan Instructions
- Write your full name on the top of the first page “Participant name:”
- Attach a completed copy of your Operational Plan to be marked.
- Attach the completed parts of your Financial Plan that are requested.
Check off the Assessment Submission Checklist
This will ensure you have completed all tasks and paperwork correctly and we won’t need to return anything before marking.
News feed



